[ad_1]
Emerging market currencies are currencies backed by emerging market countries, such as the South African Rand, Mexican Peso or Brazilian real. Traders seek them out because they are generally more volatile than developed market currencies.Highly volatile currency pairs can offer stronger and more prominent moves.
It’s important for traders to understand the core characteristics of emerging market currencies and how they differ to developed market currencies. This article will cover these in depth.
What are emerging market currencies?
The factors which make a currency an emerging market currency are debatable. Although, it is generally agreed that emerging market countries have lower GDP per capita, higher inflation and higher unemployment – amongst other factors – compared to more developed countries like the United States.
The three main characteristics of emerging markets include:
- Underdeveloped infrastructure – Roads, buildings, schools and general infrastructure need to be developed. This means that emerging market economies require more investment and have higher potential growth rates, but also higher debts.
- Younger population – The population pyramid is bottom-heavy for emerging markets. This means that there are more young people than there are old people. Emerging markets normally have increased mortality rates compared to developed countries.
- Higher levels of foreign debt – Emerging markets rely on foreign borrowing to fund investment, this is partly a reason that emerging market currencies are extremely volatile- if investors lose confidence it can lead to great depreciations in the emerging market currency.
As a result, emerging market currencies tend to be less liquid and more volatile than major currency pairs from more developed countries. It’s important for traders to recognize the unique opportunities and differences between the two. These are stated in the table below:
|
Major Currencies |
Emerging Market Currencies |
|
|
Liquidity |
Highly Liquid |
Moderately Liquid |
|
Transaction costs/Spread |
Low |
High |
|
Historical Volatility |
Low |
High |
Top 5 Emerging market currencies to watch
Mexico
The USD/MXN (US Dollar/Mexican Peso) is a popular emerging market currency amongst traders due to its volatility. The United States imports around 80% of Mexico’s exports so talk of changes in trade-agreements or tariffs can impact the Mexican Peso.
Mexico’s three biggest exports are:
- Vehicles
- Electrical machinery and equipment
- Machinery including computers
Mexico’s three biggest exports by country are:
- United States
- Canada
- Germany
Russia
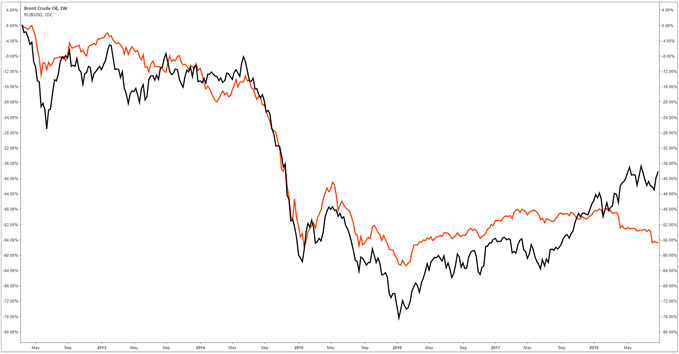
USD/RUB (US Dollar/ Russian Ruble). Russia is rich in natural resources. It is one of the largest crude oil producers in the world and a powerful member of OPEC.
Of all Russia’s exports, 48% consist of mineral fuels, oils and distillation products so the Russian Ruble is strongly correlated to the price of oil. The graph below shows the price of oil (Black graph) and the RUB/USD (USD/RUB inverse) so that if the price of RUB/USD declines it means that the Russian Ruble is getting weaker. You can see that when the price of oil decrease so does the Russian Ruble.
Russia’s three biggest exports are:
- Mineral fuels, oils, and distillation products
- Commodities
- Iron and steel
Russia’s three biggest exports by country are:
- China
- Netherlands
- Germany
India
With a population of close to 1.4 billion, India competes with China on having the highest population in the world. India’s currency is the Indian Rupee (USD/INR) and it has the fourth-largest economy in the world and it’s growing fast (see image below).
The appeal to invest in an economy like India is obvious when you look at the GDP growth from 1981-2017. The growth rate for the period averages at around 6% – a very high rate compared to developed markets and even other emerging markets.
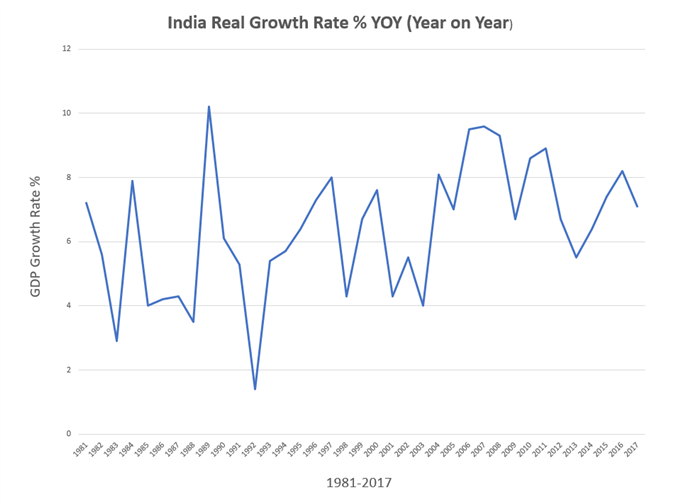
Source: Bloomberg
India’s three biggest exports are:
- Pearls, precious stones, metals, and coins
- Mineral fuels, oils, and distillation products
- Machinery, nuclear reactors, boilers
India’s three biggest exports by country are:
- United States
- United Arab Emirates
- Hong Kong
China
China is the second biggest economy in the world and it has the largest population in the world.Smaller trading partners of China tend to do a majority of their trading with China. Therefore, their economies become dependent and intertwined with China’s economy. Consider Australia for example, since 20-25% of Australia’s exports go to China, its currency (AUD/USD) is very sensitive to the economic health of Chinese economy. It’s a similar story for other small economies who trade a lot with China.
Characteristics of China’s economy:
- Largest foreign exchange reserves in the world.
- China is the world’s largest exporter.
- Largest population in the world.
As shown in the image below the Chinese Yuan trades in a band between six to seven Chinese Yuan per dollar. It is a very hard currency to trade because it does not display clear chart patterns like other currencies. Do not confuse the CNH and the CNY, the CNH is the offshore Yuan and the CNY is the onshore Yuan.
Find out more on the differences between CNH and CNY
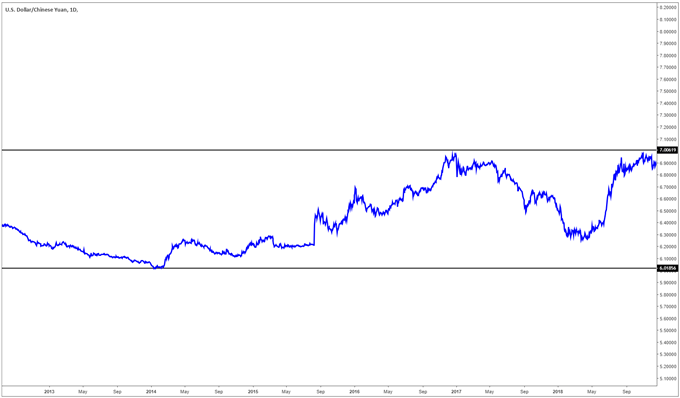
China’s three biggest exports are:
- Electrical, electronic equipment
- Machinery, nuclear reactors, boilers
- Furniture, lighting signs, prefabricated buildings
China’s three biggest exports by country are:
- United states
- Hong Kong
- Japan
South Africa
South Africa’s economy has struggled to achieve consistent growth amidst corruption scandals and rent-seeking from state owned enterprises. The USD/ZAR (US Dollar/ South African Rand) has been one of the most volatile emerging market currencies.
The South African Rand has been shown to be extremely sensitive to political risk, as in December of 2015 it depreciated almost 20% when the current president Jacob Zuma fired the Finance minister spurring a lack of investor confidence and a subsequent deterioration in the Rand.
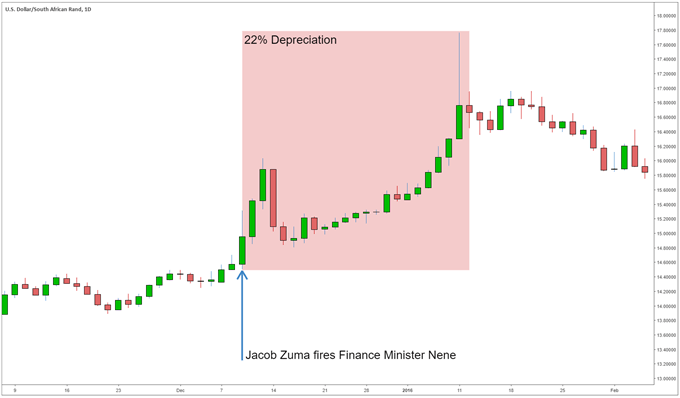
South Africa’s three biggest exports are:
- Pearls, precious stones, metals, and coins
- Ores slag and Ash
- Mineral fuels, oils, and distillation products
South Africa’s three biggest exports by country are:
- China
- United States
- Germany
Why trade emerging market currency pairs?
Emerging market currency pairs are normally more volatile than major currency pairs, this is one of the reasons why they appeal to traders because they display bigger moves.
Pros and cons of trading emerging market currency pairs include:
Pros
- Volatility: Emerging market currencies offer larger, more prominent moves.
- Diversification: Emerging market currencies offer an alternative to major currencies.
Cons
To trade emerging markets consistently, traders should be aware of up-coming political events that could spur volatility. Due to the pairs displaying higher volatility, traders could also take smaller positions to reduce the risk of being slipped. Other events that could spur volatility include economic data releases which you can keep up to date with on an economic calendar.
Emerging currencies trading tips
Tips to trade emerging market currencies include:
[ad_2]
Source link