[ad_1]
FX markets are susceptible to a range of factors which affect their volatility, and many traders look to tailor their strategies to capitalize on the most volatile currency pairs.
Volatility, usually measured using the standard deviation or variance of a currency, gives traders an expectation of how much a currency can deviate from its current price over a certain period. The higher the volatility of the currency, the higher the risk. Volatility and risk are usually used as interchangeable terms.
Different currency pairs have different volatilities. The major currency pairs like the EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD and USD/CHF generally have less volatility than the emerging market currency pairs like the USD/ZAR, USD/KRW and USD/BRL. Normally, more liquid currency pairs have less volatility.
Some traders enjoy the higher potential rewards that come with trading volatile currency pairs, although this increased potential reward comes with a higher risk, so traders should reduce their position sizes when trading highly volatile currency pairs.
What are the most volatile currency pairs?
Source: Bloomberg Data, Historical volatility, Standard deviation over 10 years of lognormal returns
Among the major currency pairs, the AUD/JPY, NZD/JPY and AUD/USD are currently the most volatile.
Source: Bloomberg Data, Historical volatility, Standard deviation over 10 years of lognormal returns
The USD/ZAR, USD/KRW, USD/BRL and other emerging market currencies pairs tend to be highly volatile due to their low liquidity and because of the risk that is inherent in emerging market economies.
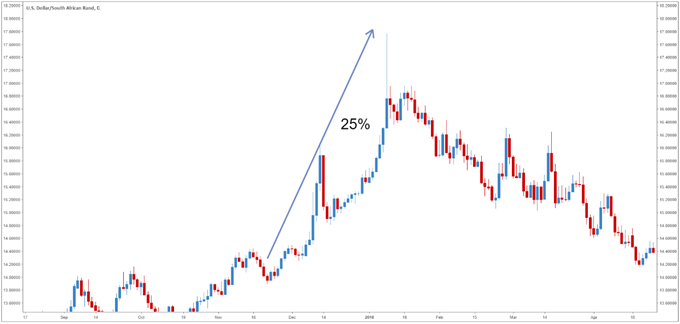
Below is an example of how volatile an emerging market currency pair can be. The USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South Africa Rand) moved 25% in a month and a half. Other emerging market currency pairs have also been seen to make these drastic moves.
What about the least volatile currency pairs?
The least volatile currency pairs tend to be the major currency pairs which are also the most liquid. Also, these economies tend to be larger and more developed which brings more trading volume to their currencies creating a tendency for more price stability.
The EUR/GBP, NZD/USD, USD/CHF and EUR/USD are the least volatile currency pairs. They are the least volatile because they trade with high volumes of liquidity.
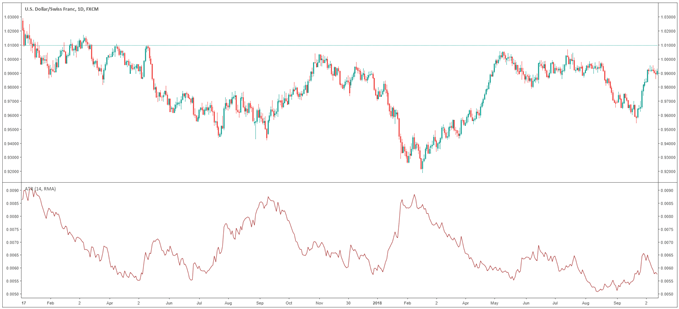
As shown below, the USD/CHF’s average true range (ATR) ranges between 90 to 50 pips, a low average true range compared to other pairs. The average true range of a currency is one of the many ways to measure the volatility of a currency pair.
Correlation between two currencies can also lead to lower volatility. For example, the US dollar and Swiss Franc (USD/CHF) are both known as safe-haven currencies (as well as the Japanese Yen) – when risk enters the market, traders flock to these currencies. Both the US dollar and the Swiss Franc strengthen relative to other currencies but do not deviate significantly from each other, and hence the currency pair does not experience as much volatility.
How to trade currency pair volatility
Forex traders should take current volatility and potential changes in volatility into account when trading. Traders should also adjust their position sizes with respect to how volatile a currency pair is. The more volatile a currency pair, the smaller the position the trader should take.
To trade volatile currency pairs, you should understand the differences between volatile currencies and currencies with low volatilities, you should also know how to measure volatility and be aware of events that could create volatility.
The difference between trading currency pairs with high volatility versus low volatility
- Currencies with high volatility will normally move more pips over a certain period than currencies with low volatility. This leads to an increased risk when trading currency pairs with high volatility.
- Currencies with high volatility are more prone to slippage than currency pairs with low volatility.
- Due to high-volatility currency pairs making bigger moves, you should determine the correct position size to take when trading them.
There are several ways to measure volatility
To determine the correct position size, traders need to have an expectation of how volatile a currency can be. A variety of indicators can be used to measure volatility like:
Read our guide to Trading Volatile Markets to find out more about volatility – how it is measured, and how it applies to other markets.
Key things traders should know about volatility:
- Big news events like Brexit or Trade wars can have a major impact on a currency’s volatility. Data releases can also influence volatility. Traders can stay ahead of data releases by using an economic calendar.
- Volatile currency pairs still obey many technical aspects of trading, like support and resistance levels, trendlines and price patterns. Traders can take advantage of the volatility using technical analysis in combination with strict risk management principles.
- Staying up to date with the latest forex pair news, analysis and prices can help you predict possible changes in volatility. At DailyFX we also have comprehensive forex forecasts to help you navigate the market.
- DailyFX hosts daily webinars which can help you prepare for volatile market times.
- Supplement your forex learning and strategy development with our New to Forex guide. Thisexplains in detail the different aspects of forex trading, from bid/ask quotes to margin and short selling.
[ad_2]
Source link